Notable Drugs of 2019
Innovation Drives Progress
Drug approvals in the last year include treatments in immunology and rare genetic diseases, as well as other innovative methods to treat depression.
Not every new drug that gets FDA approval goes on to become a big seller, but new drugs always reaffirm our belief that innovations in drug development play a key role in advancing health care for the American public.
UW-Madison’s Division of Pharmacy Professional Development offers the Drug Product Development Certificate to industry scientists and clinicians looking for a versatile survey of drug development process topics. If you are a scientist or technical manager working at the drug discovery interface, or in lead optimization and candidate selection, you may greatly benefit from this educational opportunity.
This year we have two in-person courses:
Principles of Solid Dosage Forms
Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics (PK-PD)
Without further ado, here are seven seven drugs that won FDA approval in the last year
 |
In December 2019, the FDA approved Vyondys 53 for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) with genetic mutations subject to skipping exon 53 of the dystrophin gene.
It is estimated that approximately eight percent of DMD patients have this mutation.
Vyondys 53 (golodirsen)
|
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease of the central nervous system that disrupts communications between the brain and other parts of the body.
The FDA granted approval of Mayzent (siponimod) to Novartis.
Mayzent tablets are to treat adults with relapsing forms of MS, to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease.
Mayzent is the first-ever oral drug for secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS). Up to 80 percent of patients with relapsing remitting MS develop SPMS. The challenge? Raising awareness of this stage of the disease and its symptoms, among patients and physicians.
Mayzent (siponimod)
|
 |
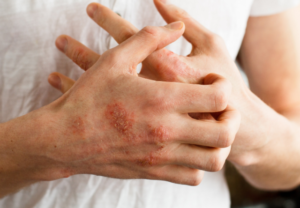 |
For the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, the FDA approved Skyrizi (risankizumab-rzaa) in April 2019.
Skyrizi has demonstrated greater efficacy in reducing psoriasis symptoms in clinical trials versus an existing market leader.
Risankizumab is also being studied for other autoimmune conditions, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Skyrizi (rizankizumab-rzaa)
|
Approved at the end of 2018, Ultomiris (ravulizumab-cwvz) offers longer intervals between injections for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) than its current medicine in the class, Soliris.
Instead of the current two-week interval for Soliris, Ultomiris is intended for dosing intervals of up to eight weeks.
The estimated average cost of Ultomiris is approximately $458,000 a year.
Ultomiris (ravulizumab-cwvz)
|
 |
|
|
Zulresso (Brexanolone), which is indicated for the treatment of postpartum depression (PPD) in adult women, is the first drug the FDA has approved specifically for this condition.
The efficacy of brexanolone was demonstrated in two multicenter, placebo-controlled studies in women aged 18 to 45 years who had PPD. In both studies patients received a 60-hour continuous IV infusion of brexanolone or placebo, and were assessed for the next four weeks.
In both studies brexanolone was superior to the placebo in improvement of depressive symptoms.
Zulresso (brexanolone)
|
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Spravato (esketamine) nasal spray in March 2019, in conjunction with an oral antidepressant, for the treatment of depression in adults who have tried other antidepressant medicines but have not benefited from them (treatment-resistant depression).
The patient self-administers Spravato nasal spray under the supervision of a health care provider in a certified doctor’s office or clinic, and the spray cannot be taken home.
This is the first FDA approval of esketamine for any use.
Spravato (esketamine HCI)
|
 |
 |
At the end of November 2019, the FDA granted accelerated approval to Oxbryta (voxelotor) for the treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD) in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age or older.
SCD is a blood disorder that causes acute pain and organ damage. It is also characterized by severe and chronic inflammation.
Oxbryta was granted Accelerated Approval, which enables the FDA to approve drugs for serious conditions to fill an unmet medical need based on a result that is reasonably likely to predict a clinical benefit to patients.
Oxbryta is an inhibitor of deoxygenated sickle hemoglobin polymerization, which is the central abnormality in sickle cell disease.
Oxbryta (voxelotor)
|
2019 brought many pharmaceutical innovations, more than we can review here. Nevertheless, today’s systems need to be faster, more reliable, and more flexible than ever. Professional development is key to help you develop new skills and gain the confidence to drive and lead innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
Visit our Drug Product Development Certificate page to learn more about how this continuing education opportunity can help your professional growth.
Continuing Education for Pharmaceutical Scientists