The Trouble With Biologics: Analyzing Large Molecules and Data Integrity
For decades there have been a small but effective number of approved biologics. However, biologics are now grabbing a larger share of drug development resources. Small molecules dominate the prescription market (more than 90% of the top 200 drugs in the USA). However, biologics are growing at a faster pace. More biologics are entering the clinic and eventually the market.
It is forecast that biologics will comprise 50% of the top 100 drugs by 2021. Whether the 50% is reached or not, the number of biologic products is definitely growing. The growth of biologics (and biosimilars) means that more attention must be given to them. There is a need to focus on the analytical techniques used in the development and approval of biologics.
Analytical challenges of biologics
Biologic molecules are significantly larger than small molecules. At 3000-150,000 Daltons (vs. less than 900 Daltons) biologics are complex for analysis. 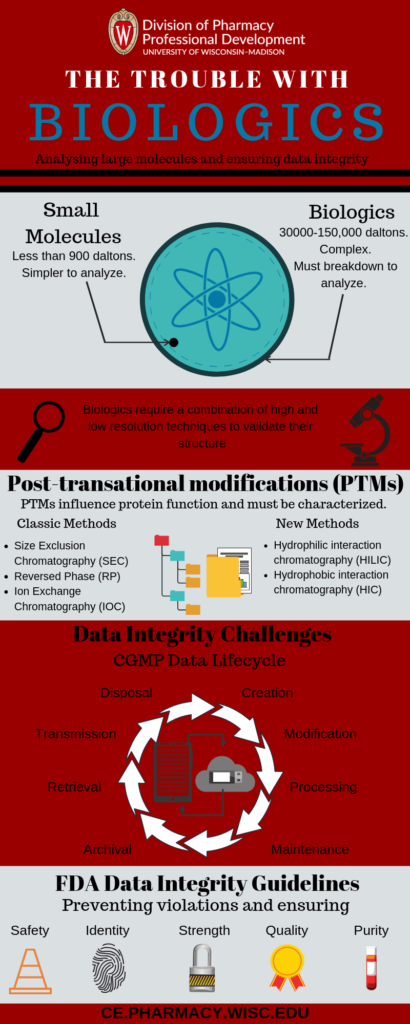
Proteins are much more heterogeneous than small molecules and require more analytical techniques. Proteins often need to be broken down using various sample preparation techniques. This breakdown is essential for obtaining the necessary analytical outcomes.
In addition, biologics need to be characterized in multiple ways. Some of these ways include stability, purity, and function. Small molecules can be structurally confirmed via high-resolution methods. (e.g. X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy). But biologics require a combination of high and low-resolution techniques to validate their structures.
The complex nature of the recombinant production means that there are many post-translational modifications (PTMs) generated. PTMs directly influence protein function. To retain only the desired modifications, PTMs must be characterized.
Protein characterization requires a variety of analytical techniques to be sequenced together. These techniques include “classic” chromatographic methods like:
- Size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
- Reversed phase (RP)
- Ion exchange chromatography (IEX)
They also include newer methods like:
- Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC)
- Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC)
Coupling these separations with high-resolution mass spectrometry leads to PTM identification. These extra steps add complexity, cost and time to analysis efforts. With the growth of large molecule therapies, the workload on analytical laboratories is increasing.
Molecular analysis isn’t the only challenge facing pharmaceutical scientists. The drug development process generates a large amount of data. Data integrity is critical throughout the Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) data life cycle. This includes data creation, modification, processing, maintenance, archival, retrieval and transmission. After the record’s retention period is complete data disposition is also essential.
Errors, omissions, and aberrant results must be easily detected throughout the data’s life cycle. System designs and controls need to enable efficient detection. An acronym describing ideal data integrity attributes is ALCOA (attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded, original, and accurate).
The FDA and Data Integrity Violations
In December 2018 the FDA released a data integrity guidance. The FDA has observed increased data integrity violations during CGMP inspections in recent years. This is troubling because ensuring data integrity is an important responsibility. Data integrity ensures the safety, efficacy, and quality of drugs. Data integrity failures could impact public health.
These data integrity-related CGMP violations have led to many regulatory actions. These actions include warning letters, import alerts, and consent decrees. The underlying premise is that CGMP sets forth minimum requirements. This ensures that drugs meet the standards of the FD&C Act:
- Safety
- Identity
- Strength
- Quality
- Purity
All records required under CGMP are subject to FDA inspection. Training personnel on proper data handling is required. The FDA requires that workers have the education, training, and experience to perform their assigned duties.
2019 Annual Pharmaceutical Analysis Conference
The August Land O’Lakes Conference has offered practical information for analytical scientists for 58 years. The 59th Annual Pharmaceutical Analysis Conference theme is “Addressing Technical and Regulatory Challenges in Pharmaceutical Analysis”. Portions of this year’s conference will focus on data integrity. You will learn about analytical solutions to large molecules and approaches for achieving laboratory efficiency. This is a great opportunity to learn from regulators and industry experts. You will receive practical advice on avoiding regulatory issues and ensuring drug quality. You will not want to miss this opportunity to advance large molecule pharmaceutical analysis.
Join us at the Fluno Center on the UW-Madison Campus from August 12-15, 2019.
The Land O’Lakes series is a premier conference series for pharmaceutical scientists. With over 60 years of experience, it is one of the oldest and most respected conference series. In addition to the Pharmaceutical Analysis Conference, the 2019 Land O’ Lakes series includes the Bioanalytical Conference (July 15-18, 2019) and DMPK Conference (September 9-12, 2019).
Discover all Land O’ Lakes Conferences
References
http://www.chromatographyonline.com/lcgc-blog-large-molecule-analysis-small-molecule-people
http://www.pharmtech.com/changing-industry-brings-new-challenges-also-opportunities
